Tritium (3H or T) is an isotope of hydrogen with 2 neutrons and 1 proton. It is unstable, decaying by emitting an electron with a decay energy of only 18.6 keV. That's the kind of energy electrons have in a cathode ray tube television. In most cases, the antineutrino which forms at the same time an electron does carries away some of that energy, so emitted electrons carry even less energy. Its radiation is less hazardous than its mass, which causes 3H to metabolize differently from 1H. (Obviously, metabolic damage hasn't been shown with 3H, but it has with 2H(1).) Tritium is safe enough to use in applications such as self illuminating signs or egress lights.
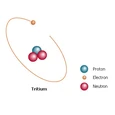
The structure of tritium.